The Framework for Responsible and Ethical Enablement of Artificial Intelligence (FREE-AI) Committee was established by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) to direct the financial industry’s adoption of AI. India faces both enormous opportunities and greater risks as AI quickly advances from rule-based systems to generative models. By enhancing fraud detection, credit evaluation, customer interaction, and oversight tools, artificial intelligence (AI) can significantly benefit finance. Generative AI can create synthetic datasets for safer model training, automate reporting, and customise customer support. AI that is multilingual and multimodal could help bridge gaps for underserved communities across diverse languages and literacy levels.
Opportunities in AI adoption
The Committee’s report identifies a number of potential areas where AI has an opportunity to transform the industry. Automating repetitive tasks, lowering operating expenses, and facilitating quicker, data-driven decision-making can significantly increase efficiency. As AI models use alternative data sources, like utility payments or mobile phone usage, to evaluate creditworthiness for borrowers with little to no traditional credit history, financial inclusion could see a major boost. AI integration with India’s robust digital public infrastructure, including Aadhaar and UPI, may make it possible to provide inclusive and highly customised services. The report also highlights the necessity of creating local AI models that are suited to India’s operational diversity and multilingualism. This strategy will assist in preventing the industry from becoming unduly reliant on foreign technologies.
Risk and challenges
The report emphasizes that, despite its potential, artificial intelligence also presents a complex risk environment. Accuracy and fairness can be harmed by model risks such as bias, ambiguity, and data errors. When automation leads to more errors or when AI systems deteriorate over time without adequate supervision, operational risks occur. An institution’s control over compliance may be restricted and concentration risks may arise from an excessive reliance on cloud providers and third-party vendors. In the AI age, cybersecurity risks such as data poisoning, adversarial attacks, and deepfake fraud are increasing. Public trust can be harmed by ethical problems like algorithmic bias and consumer choice manipulation. A more general worry is that a strong dependence on comparable AI models may lead to “herding” behaviour, which would raise market volatility.
The FREE AI Framework
Trust is the foundation of ethics, followed by:
- People First
- Innovation over Restraint
- Fairness and Equity
- Accountability
- Understandable by Design
- Safety
- Resilience
- Sustainability
These guidelines stress that the adoption of AI in finance is predicated on trust. Even the best technology won’t be able to get traction without it.
The Committee suggests six strategic pillars that combine risk management and innovation in order to put these ideas into practice. The Infrastructure pillar advocates for innovation sandboxes and shared AI facilities. Sector-specific frameworks and unambiguous regulatory guidance are the main objectives of the Policy pillar. In order to increase institutional readiness, capacity emphasises the necessity of AI training and knowledge exchange across industries.
The FREE-AI Committee aims to create a robust financial ecosystem that fosters innovation. The financial sector in India can leverage AI’s transformative potential while maintaining systemic stability and public trust by implementing the Six Strategic Pillars and establishing AI adoption in the Seven Sutras. The key takeaway is that responsible AI is about making sure that protection and advancement complement one another, not about picking one over the other.
Shape the future of AI in finance with confidence. For expert guidance on RBI’s FREE-AI framework, ethical AI adoption, and AI risk assessments, visit www.tsaaro.com.
News of the week
- Anubis Ransomware Wipes Files, Increasing the Threat by Low Skilled Attackers
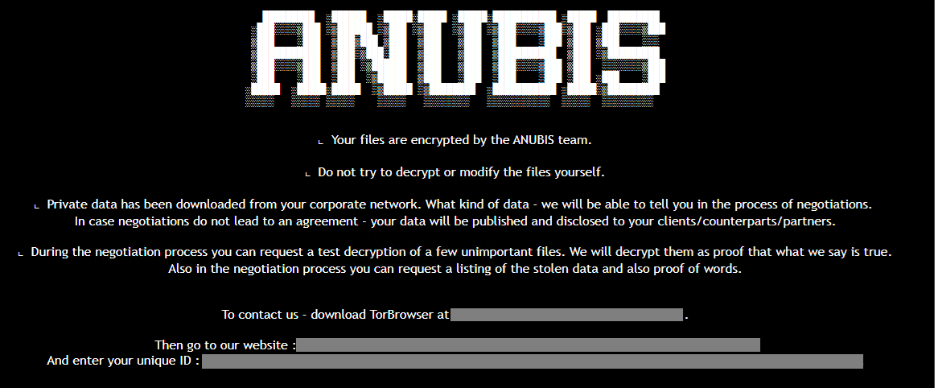
Anubis, a sophisticated Ransomware-as-a-Service (RaaS) operation, has emerged as a highly destructive cyber threat, which, unlike typical ransomware that only encrypts files to demand payment for a decryption key, goes a step further and also wipes data. The data destroyed by Anubis is nearly impossible to recover, even if the ransom is paid. The operation is marketed to cybercriminal affiliates on underground forums, offering them the malicious tools and infrastructure in exchange for a share of the ransom profits. Anubis primarily targets Windows systems, exploiting multiple infection vectors including phishing emails, malicious attachments, and exploited vulnerabilities. The RaaS model makes Anubis accessible to low-skilled attackers, significantly broadening its threat landscape. Its operators employ advanced evasion tactics to bypass endpoint detection and response (EDR) systems, making it harder for organisations to defend themselves.
- ShinyHunters Cybercrime Group Linked to Major Data Breaches
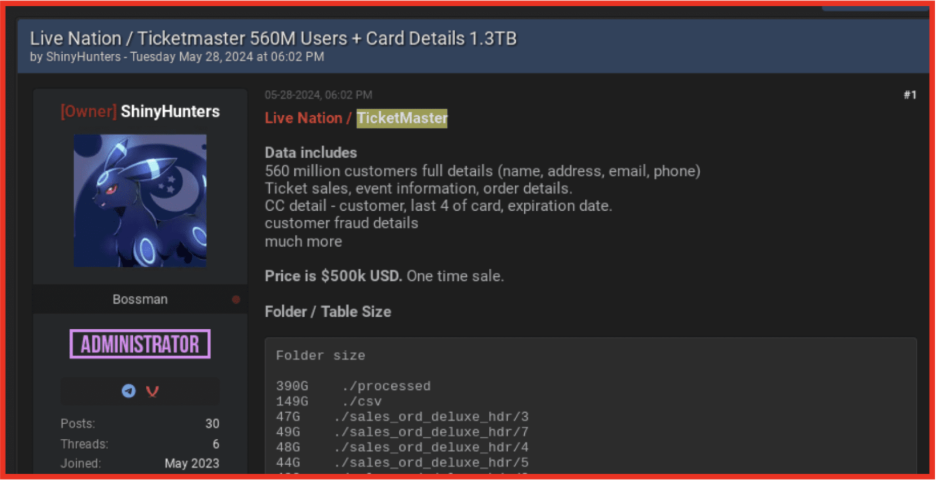
U.S. authorities have charged Sebastien Raoult, a 23-year-old from France, who pleaded guilty to his involvement in the cybercrime group, popularly known as ShinyHunters. This group has been linked to the theft and sale of hundreds of millions of user records worldwide. Since at least 2020. They are famous for breaking into major companies and stealing sensitive data and later selling it on dark web marketplaces. Prosecutors claim Sebastian and Esco conspired to target more than 60 companies in various countries throughout their operations and have stolen names, passwords, financial details and many other personal information from individuals. This group was actively involved in the significant leagues related to Microsoft Git Hub repositories in 2020. Sebastian faces sentencing with long-term prison time, and U.S. officials see this case as a part of a larger effort to respond to transnational cybercrime groups.
https://thehackernews.com/2025/08/cybercrime-groups-shinyhunters.html
- Cabinet Approves Semiconductor Manufacturing Units in Odisha, Punjab, and Andhra Pradesh
The Union Cabinet has approved the establishment of three semiconductor manufacturing units with a total investment of ₹4,600 crore, aimed at boosting India’s electronics and chip production ecosystem. These projects are expected to strengthen India’s position in the global semiconductor supply chain and will create skilled jobs and support critical sectors like automotive, consumer electronics and clean energy. This initiative alliance with the governments Semicon India programme which was created to promote self-reliance and strategic technology manufacturing. The main project is a combination of three projects, namely continental device, India and its expansion plans in Mohali, Punjab., tata semiconductor assembly and test Private Limited, which will set up an advanced semiconductor packaging and testing unit in Odisha, CG power and industrial solutions Limited, which will establish a unit in Andhra Pradesh for manufacturing silicon car by devices.


